Disadvantages of renewable energy

Renewable energy is derived from natural resources that can be replenished indefinitely without the risk of depletion and harmful emissions. These sources include solar power, wind, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal.
Renewable energy sources have gained well-earned attention over the decade as they are dependent on unlimited sources, which do not contribute to health and environmental issues.
In 2022, the world generated 28,517.83 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, of which about 30% came from renewables. Figure 1 exhibits the total electricity generation worldwide from 1985-2022 along with the percentage coming from renewable energies in the same timeline.
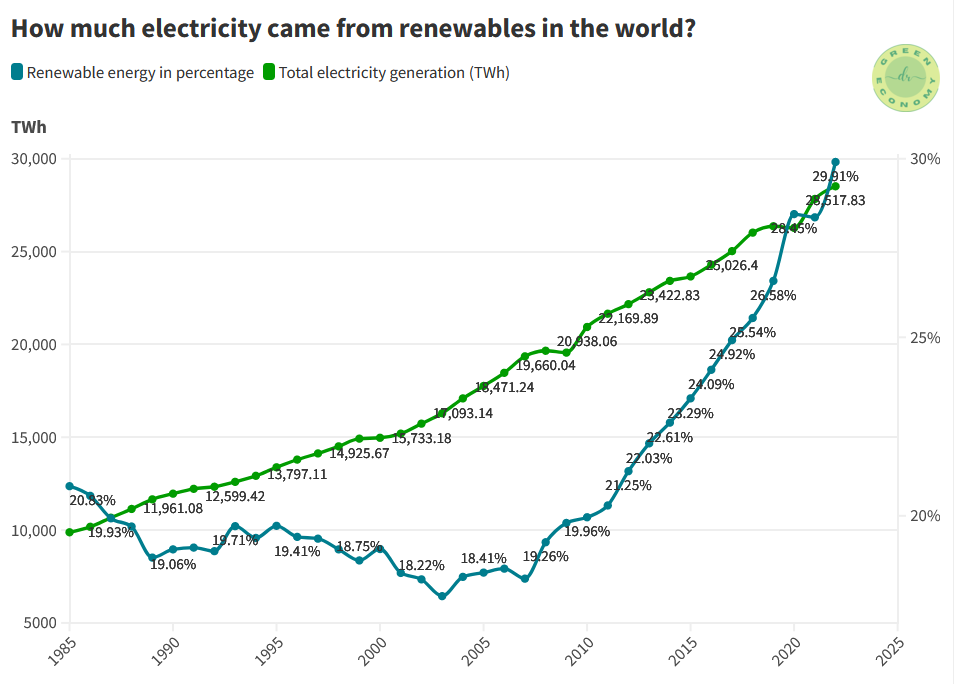
Although the trend line has gone down until 2007, the percentage of renewable energy has gone up continuously after that, reaching about 30% in 2022 from 18.24% in 2007.
Looking at the year 2022 in Figure 2, 35.8% of the electricity generation worldwide came from coal because in most industrialized nations, the reliance on traditional fossil fuels as the primary energy source persists.
Hydro with 15.2% became the highest percentage representing renewable energies. Solar and wind represented 4.5% and 7.5%, respectively.
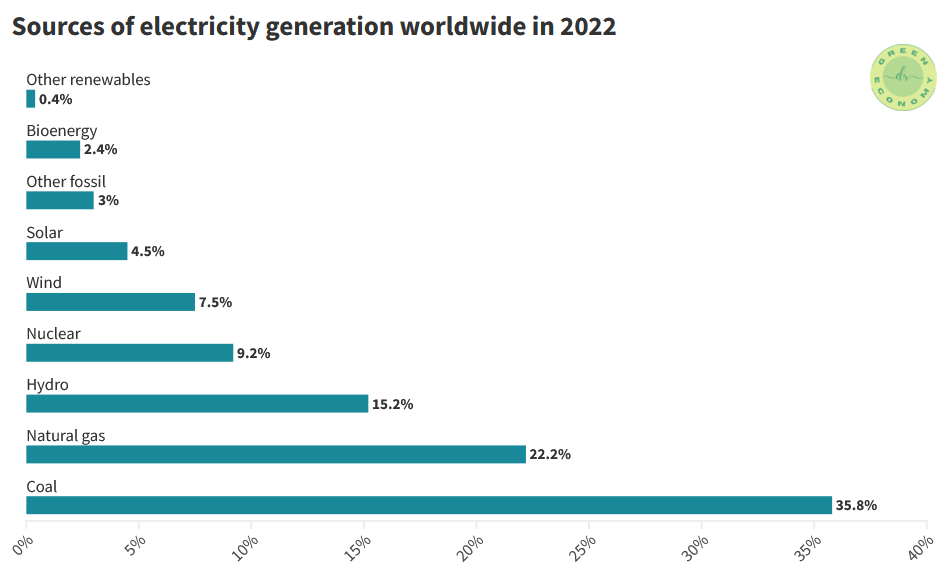
Together with nuclear energy, renewables accounted for about 39% of the global electricity generation. According to McKinsey's analysis, global renewable-electricity capacity is expected to witness a substantial increase of over 80% from 2020 levels by 2026.
Notably, two-thirds of this growth will be driven by wind and solar power, experiencing a remarkable surge of 150%. Projections suggest that by 2035, renewables will contribute 60% of the world's electricity generation.
Top renewable energy producing countries
The widespread adoption of renewable energy plays a crucial role in tackling climate change and minimizing the impacts associated with this global phenomenon. In 2022, China, the United States (US), and Brazil emerged as the top countries in terms of installed renewable energy capacity (Figure 3).
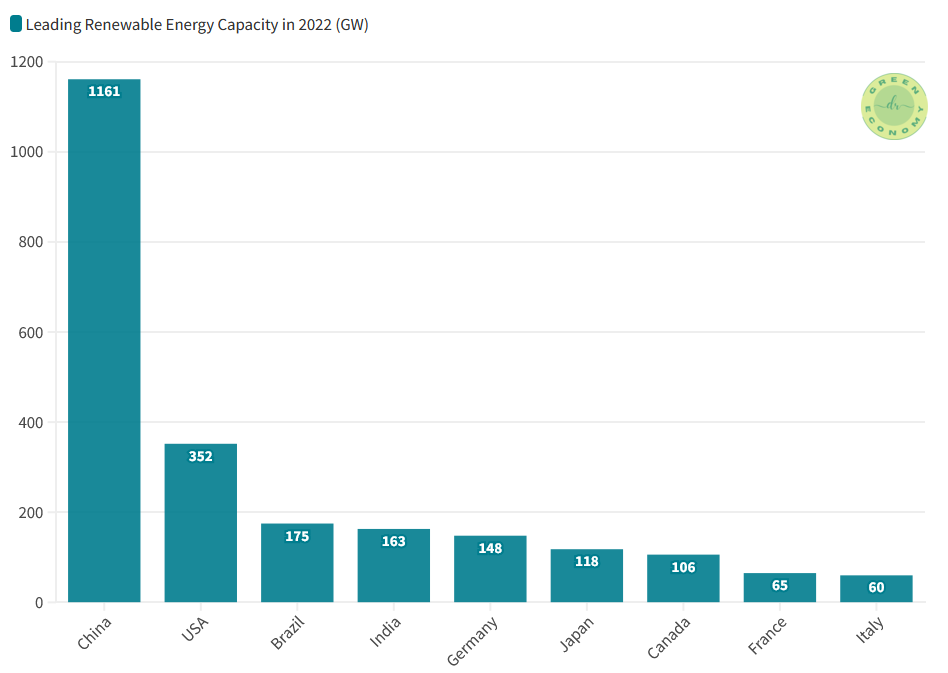
China secured the leading position, boasting an impressive capacity of approximately 1,161 gigawatts (GW). The US followed behind, with a capacity of around 352 GW, followed by Brazil with 175 GW.
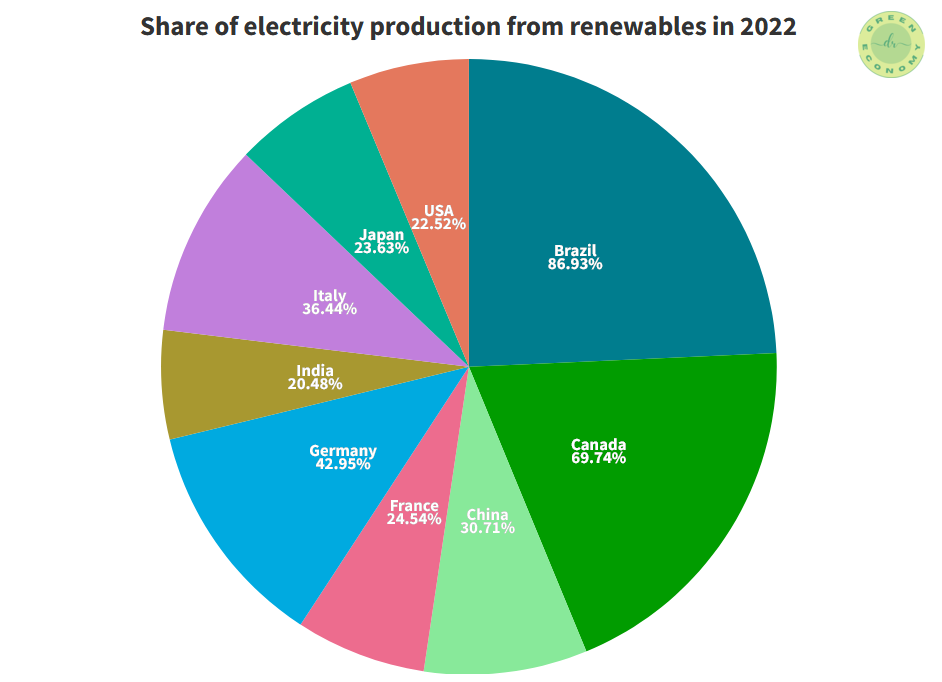
The share of electricity production from renewables of the top 9 countries listed in Figure 3 is shown in Figure 4. China, which had the leading renewable energy capacity with 1161 GW only had a 30.71% share of electricity production from renewables.
Brazil, with only a capacity of 175 GW had 86.93% of its energy production coming from renewables.
These countries are realigning their business models, investing in renewables, electrification of vehicles, hydrogen and ammonia production, decarbonization of steel manufacturing, and powering their operations and manufacturing through renewables.
Moving forward, renewable energy, specifically wind and solar power, is anticipated to take a crucial role in the global energy supply as nations diligently pursue ambitious decarbonization goals.
Solar energy will lead by 2050
According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), solar power is projected to play a larger role in global power generation over the next three decades, driven by the increasing global adoption of renewable energy while hydroelectric power expands at a slower pace, as shown in Figure 5.
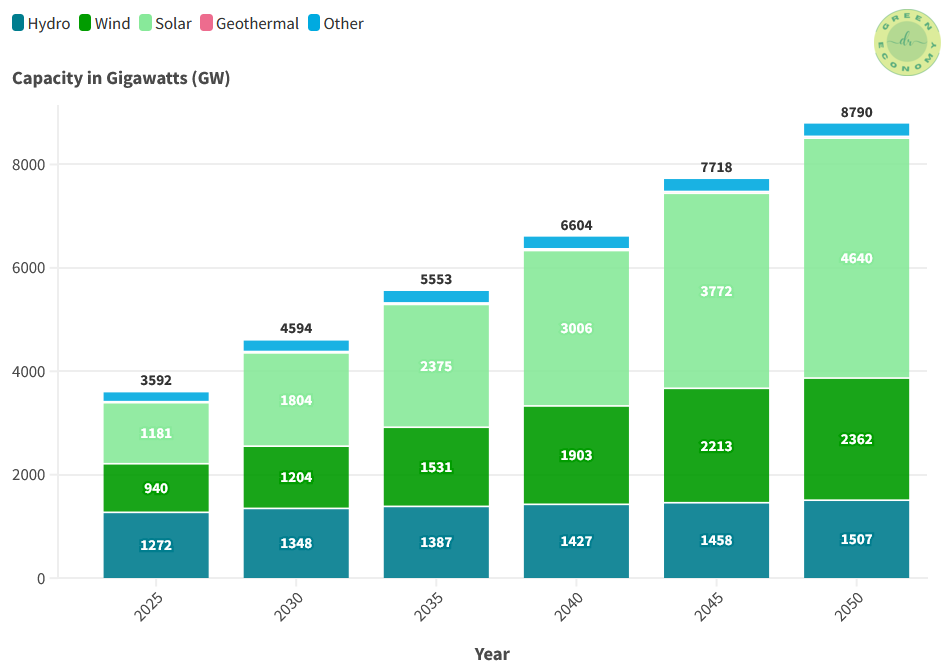
Wind energy is also expected to experience notable growth, with global capacity witnessing a significant increase over the past decade.
The EIA expects China to experience substantial solar power growth due to rising electricity demand, supportive government policies, and lower manufacturing costs of solar technology in the country.
Geothermal (too small to see in Figure 5) has a small amount to contribute compared to other renewables. From 2025-2050, it is expected to be in charge of 19-34 GW.
Hydropower, on the other hand, is considered a mature technology, with most of the optimal hydro sites already utilized. In this case, China and Canada stand out as the top two countries, producing the highest amount of energy.
Read: Solar energy facts: a win-win for businesses and the planet
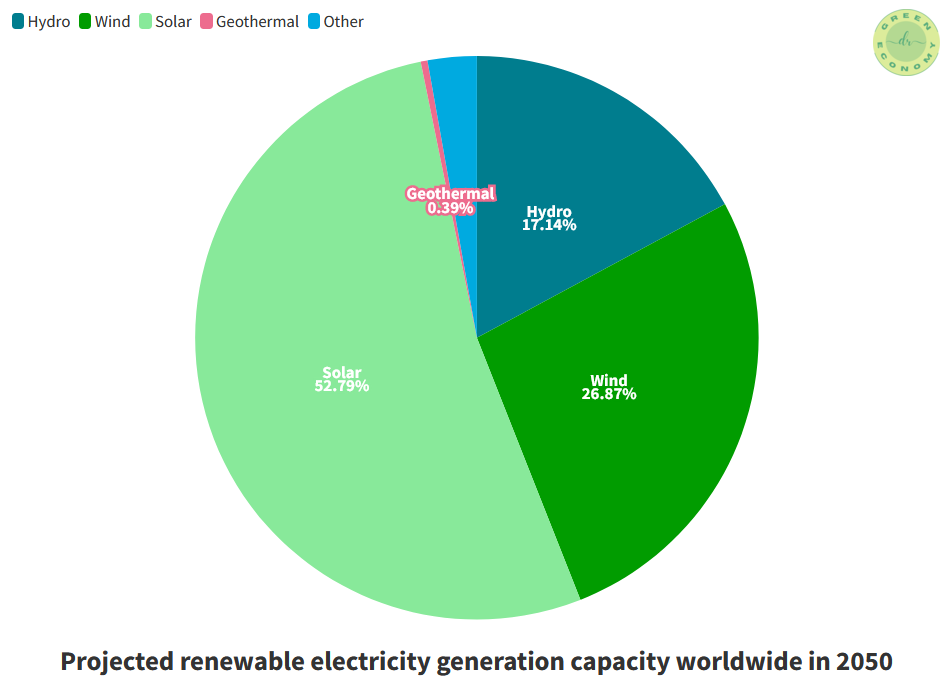
In the year 2050, it is anticipated that the installed capacity of solar power will surpass 4.6 TW which is equivalent to 52.79% of the total projected renewable energy generation capacity (Figure 6). Wind power is expected to rank second with approximately 26.87%, followed by hydropower at 17.14%.
Interestingly, solar energy has also received a significant boost with the development of an "ultra-thin" device capable of converting stored energy into electricity. In 2017, a group of researchers from a Swedish university developed an innovative energy system capable of capturing and storing solar energy for a span of 18 years, subsequently releasing it as heat whenever required.
This concept holds the potential to pave the way for self-charging electronics that can utilize stored solar energy on demand.
Disadvantages of renewable energy
- Relies heavily on weather conditions. When adverse weather conditions occur, renewable energy technologies like solar cells may not be as effective. For example, during periods of rain, PV panels cannot generate electricity, necessitating a shift back to traditional power sources.
- Lower efficiency. Regrettably, renewable technologies generally exhibit lower efficiency compared to traditional energy conversion devices. For example, commercially available solar panels have an efficiency of about 15% to 20%. In contrast, traditional technologies utilizing coal or natural gas can achieve efficiency levels of up to 40% and 60% respectively.
- High upfront cost. The manufacturing and installation processes for renewable energy devices, such as PV panels, can be relatively expensive. Only for installation, solar panels cost about $17,430 to $23,870 on average.
- Limited geographical region. The availability of high-quality land is limited, leading developers to urgently search for new sites. For example, in Germany, regulatory, environmental, and technical limitations significantly reduces the potentially suitable for onshore wind farms to just 2%.
- Shortages of key raw materials. This includes essential metals like nickel, copper, and rare earth metals, such as neodymium and praseodymium, which are vital for the creation of magnets used in wind turbine generators.
The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is essential for long-term sustainable development. However, it requires effective measures and feasible, cost-effective technological advancements in energy harvesting.
Summary
- In 2022, around 30% of global electricity generation came from renewables, with hydro being the largest contributor followed by wind and solar
- Brazil, Canada, and China have shown leadership in transitioning to renewables
- Solar power is projected to play a major role in global power generation by 2050
- Some disadvantages include reliance on weather conditions, lower efficiency, high upfront costs and limited geographical availability